“UbuntuHelp:UsingTheTerminal/zh”的版本间的差异
来自Ubuntu中文
Dbzhang800(讨论 | 贡献) 小 |
小 (→更改命令) |
||
| (未显示24个用户的51个中间版本) | |||
| 第3行: | 第3行: | ||
{{From|https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UsingTheTerminal}} | {{From|https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UsingTheTerminal}} | ||
| − | {{Translator| | + | {{Translator|casm}} |
| − | + | {{Languages|UbuntuHelp:UsingTheTerminal}} | |
| − | + | === 为什么使用终端? === | |
| + | |||
| + | Linux下面有多种GUI(图形用户界面),可以在其下点击鼠标,拖拽,能够很好的工作却不需要一次读很多文档.而传统的Unix环境是 CLI(命令行界面),即在命令行下键入命令,执行想要的操作。相比之下,这种方式执行起来更快,功能也更强,不足之处是用户需要了解相关操作的命令。 --摘自 man intro(1) 在做某些任务,特别是系统配置等任务时使用终端是很有意义的,或许在帮助页或 [http://www.ubuntuforums.org 论坛]中你已经看到过类似这样的指令: | ||
<pre>sudo gobbledegook blah_blah -w -t -f aWkward/ComBinationOf/mixedCase/underscores_strokes/and.dots | <pre>sudo gobbledegook blah_blah -w -t -f aWkward/ComBinationOf/mixedCase/underscores_strokes/and.dots | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | 通常假设你知道怎么使用终端-而且任何人都能输入和退格。但有一些快捷的方法使你的生活更容易一些: | |
| − | * | + | * 怎样在终端窗口中移动和编辑你输入的文字。 |
| − | * | + | * 一些基本的Linux命令。 |
| − | * | + | * 打开终端的不同方法,怎样同时操作好几个终端,等等。 |
| − | === | + | === 使用本页将:=== |
| − | * | + | * 本文将指导您熟练掌握基本的 GNU/Linux shell 命令。 |
| − | * | + | * 本文并不是命令行的完整教程,仅仅是对 Ubuntu图形界面工具的补充。 |
| − | * | + | * 所有命令都用黑体'''标明。''' |
| − | * | + | * 需要键入的命令用“引用黑体”'''标明。''' |
| − | * | + | * 本文的所有命令都要在终端下执行。 |
| − | * ''' | + | * 注意:Linux是大小写敏感的。'''User,user,USER在Linux是不同的。''' |
| − | === | + | === 启动终端 === |
| − | ==== | + | ==== 在 Gnome (Ubuntu) 中 ==== |
| − | + | ;从“应用程序”菜单启动:终端位于 '''应用程序''' -> '''附件''' -> '''终端'''。 | |
| − | + | [[File:terminal.png]] | |
| − | + | ;使用命令启动: 按Alt-F2,输入 gnome-terminal 回车 | |
| − | + | [[File:alt_f2_terminal.png]] | |
| − | + | ;使用热键: 在键盘快捷键中设置自己习惯使用的热键,每次按热键就可启动终端。 | |
| − | + | [[File:run_from_hotkey.png]] | |
| − | ==== | + | ==== 在 Xfce (Xubuntu) 中 ==== |
| − | + | 终端位于 '''应用程序''' -> '''系统''' -> '''终端'''。 | |
| − | ==== | + | ==== 在 KDE (Kubuntu) 中 ==== |
| − | + | 终端位于 '''K菜单''' -> '''系统''' -> '''终端程序 (Konsole)'''。 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | === 命令行 === |
| − | * ''' | + | ==== sudo:需要提升权限执行的命令 ==== |
| − | * '''du''' | + | |
| − | + | * 如果您所在的目录或想操作的文件不在您的帐户所在的目录,下面的大多数命令都需要使用 '''sudo'''命令。这是一个特殊的命令,它给你临时的权限来修改系统设置。终端会询问你的密码。sudo 使用详情请参阅[[UbuntuHelp:RootSudo|RootSudo]] | |
| − | 1032 /media/floppy/files | + | |
| − | 1036 /media/floppy/ | + | ==== 文件 & 目录类命令 ==== |
| − | user@users-desktop:~$ du -sh /media/floppy | + | |
| − | 1.1M /media/floppy/ | + | * '''pwd''':'''pwd''' 命令查看您当前所处的路径('''pwd''' 代表 "打印当前工作目录")。例如:在桌面文件夹中执行 "pwd" 命令将输出 "~/Desktop"。注意,Gnome 的终端在窗口标题中也会显示这一信息-具体请看本页顶部的截屏图片。 |
| − | + | ||
| − | * '''-s''' | + | * '''ls''':'''ls''' 命令列出当前目录下的文件(和目录)。使用特定的参数,您可以查看文件的大小,创建时间,权限等。例如:'''"ls ~"'''会列出您的home目录中的文件(和目录)。 |
| − | * '''free''' | + | 如:ls -a表示“列出所有文件,包括以 "." 开头的隐含文件”。 |
| − | * '''top''' | + | |
| − | * '''uname -a''' | + | * '''cd''':'''cd'''命令用来改变当前工作目录。当您打开一个终端的时候,您就位于您的home目录中。如果想要切换到其它的目录,就要用 '''cd'''命令。例如: |
| − | * '''lsb_release -a''' | + | * 进入root目录,输入 '''"cd /"''' |
| + | * 进入到您自己的目录(home目录),输入 '''"cd"''' | ||
| + | * 进入当前目录的上一层目录,输入 '''"cd .."'''(译者注:cd 与 .. 之间有空格) | ||
| + | * 进入前一个操作的目录,输入 '''"cd -"''' | ||
| + | * 一次进入多层目录,输入 '''"cd /var/www"''',将会直接切换到/var的子目录/www中。另一个例子, '''"cd ~/Desktop"'''将会进入到您的桌面目录 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''cp''':'''cp'''命令用来复制文件。例如:'''"cp file foo"'''命令将会创建一个"file"的精确的副本,并命名为"foo",而 "file"不会有任何变化。如果是复制目录,那就得用'''"cp -r directory foo"'''(递归地复制)。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''mv''':'''mv'''命令将文件移动到另一个位置或者给文件更名。看下面的例子:'''"mv file foo"'''命令会将文件"file"更名为"foo"。'''"mv foo ~/Desktop"'''会将文件"foo"移动到桌面目录,但不会更名。如果想更名,你必须要指定一个新的名字。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 为了输入方便,您可以用 '~' 符号来代替您的home目录。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 如果在用mv命令的时候前面加上了sudo,那么“~“这个符号将可以正常使用,终端会把他替换成你自己(普通用户)的home目录。而如果你用”sudo -i“或者”sudo -s“,'sudo su'打开了一个root用户的终端,那么这时”~“将指代root用户的home目录,而非你自己的。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''rm''':这个命令用来移动或删除文件。对于非空的目录,需要rm -r才能删除。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''rmdir''':命令'''rmdir'''只能用来删除“空”目录。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''mkdir''':'''mkdir''' 命令用来创建目录。例如:'''"mkdir music"'''将会创建一个 music 目录。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''man''':'''man''' 命令用来显示其它命令的手册页。执行 '''"man man"'''可以查看到 man自己的信息。通过 "'''Man''' & Getting Help"能够分页显示更多的信息。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== 系统信息类命令 ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''df''':'''df'''命令用来查看各个文件系统当前的空间使用状况。'''"df -h"'''可能是最有用的选项了-它以M和G为单位输出,而不是以块为单位。('''-h''' 的含义是“便于阅读”) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''du''':'''du'''命令可以显示某一个目录使用了多少磁盘空间。它可以显示该目录中的各个子目录分别使用了多少空间,也可以显示当前目录一共占了多少空间。例如: | ||
| + | user@users-desktop:~$ du /media/floppy | ||
| + | 1032 /media/floppy/files | ||
| + | 1036 /media/floppy/ | ||
| + | user@users-desktop:~$ du -sh /media/floppy | ||
| + | 1.1M /media/floppy/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''-s''' 代表”概况、总览“,'''-h''' 则代表”易于人阅读“。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''free''':'''free'''命令用来查看系统中使用和剩馀的内存情况。'''"free -m"''' 将结果以M为单位输出,这对现在的计算机来说非常有用。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''top''':'''top''' 命令用来查看linux系统的信息,运行着的进程和系统资源,包括 CPU、内存以及交换分区使用情况和运行着的任务的总的数量。退出 top ,按'''"q"'''。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''uname -a''':'''uname'''命令的 '''-a''' 参数用来查看系统的所有信息,包括 机器名,内核名称 & 版本 和一些其它的细节。它最大的用处是用来查看当前所用内核的信息。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''lsb_release -a''':'''lsb_release'''命令的'''-a'''参数查看当前运行的linux的版本信息,例如: | ||
<pre>user@computer:~$ lsb_release -a | <pre>user@computer:~$ lsb_release -a | ||
No LSB modules are available. | No LSB modules are available. | ||
| 第86行: | 第114行: | ||
Codename: dapper | Codename: dapper | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | * '''ifconfig''' | + | * '''ifconfig'''显示当前系统的网络接口信息。 |
| − | ==== | + | ==== 添加新用户 ==== |
| − | * '''"adduser newuser"''' | + | * '''"adduser newuser"'''命令用来创建一个用户名为"newuser"的新用户,为新用户 newuser 创建一个密码,使用如下命令'''"passwd newuser"'''。 |
| − | === | + | === 选项 === |
| − | + | 命令的默认操作常常会被指定一个确定的 '''--参数'''所修改。例如'''ls'''命令有一个'''-s'''参数,因此 '''"ls -s"'''就会额外的显示出文件的大小。它也有一个 '''-h'''参数,将文件的大小以很好的可读性的格式输出。参数可以以簇聚合,比如 '''"ls -sh"'''和'''"ls -s -h"'''的效果相同。大多数的参数都很长,两个破折号前缀代表一个参数,所以'''"ls --size --human-readable"'''也和上面得命令相同。 | |
| − | === | + | === 'Man' 和 获得帮助 === |
| − | + | '''man ''command''''', '''help ''command''''','''info ''command''''' and '''''command'' --help'''是命令行下面最重要的工具。 | |
| − | + | 在linux下面,几乎每一个命令和每一个应用程序都会有一个man(manual)文件,所以只要简单的键入'''"man "command""'''就能看到这个命令的手册页。例如,'''"man mv"'''会打开mv (Move) 的手册页。 | |
| − | + | 利用键盘上的方向键移动手册页面,用'''"q"'''退出。 | |
| − | + | '''"man man"'''会查看'''man'''命令的手册页,这里是一个很好的开始! | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''"man intro"'''也非常有用 -它能够查看 "用户命令介绍",写的非常好!是一份很简单的linux命令的介绍。 | |
| − | + | 还有一个就是'''info'''命令了,它通常比'''man'''还深入。输入'''"info info"'''命令可得到info页的介绍。 | |
| − | + | 一些软件开发人员喜欢用 '''info''' 而不是 '''man''' (例如Debian和GNU开发人员)。所以,如果你发现一个不很常见的命令或者程序没有 '''man''' 页面,那么就试试 '''info''' 页面。 | |
| − | + | 几乎所有的命令都能接受一个'''-h'''(或 '''--help''')选项,能够输出命令的简要的描述和参数,然后自动退回命令提示符。可以输入'''"man -h"'''或'''"man --help"'''查看。 | |
| − | + | 警告:一些软件不认为 '''-h''' 选项代表帮助,虽然少但是存在这种情况。这时候可以先试试 '''man''' 或者 '''info''' 页面,以及使用较长的选项 '''--help'''。 | |
| − | ==== | + | ==== 搜索man文档 ==== |
| + | |||
| + | 如果您不确定用哪个命令或程序,您可以试试搜索'''man'''文件。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''man -k ''foo'' '''会搜索关于foo的man文件。试试看'''"man -k nautilus"'''是怎样的。 | ||
| + | *注意:这同'''apropos''' 命令是一样的。 | ||
| + | *'''man -f ''foo'' '''仅仅搜索系统man文件的标题。试试'''"man -f gnome"'''。 | ||
| + | *这个同 '''whatis'''命令是相同的。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <Why the man / info command are English, beyond many people's comprehension including me. Can we develop a native(i.e. Chinese) edition?> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 其他有用的东西 === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==== 更加漂亮的使用手册页面 ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | 安装了Konquerer的用户会高兴的发现他们可以在Konqueror的地址栏里面输入“man:/command”,达到类似在一个web浏览器中像浏览网页一样的阅读或搜索“man使用手册”的相关信息,通过选择字体与颜色(系统配置中的字体与颜色)来达到一定程度的美化,这会让部分需要阅读大量“man使用手册”内容的用户感到一些轻松。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== 命令行中粘贴 ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | 通常,你会碰到这种情况:需要把一些网页中看到的命令粘贴到命令行窗口(也就是“终端”)里面,但你会奇怪为什么在网页上使用了“Ctrl+C”进行了复制,然后在“终端”里面使用“Ctrl+V”(粘贴)却不好使,非得自己亲自动手敲那些繁琐的命令字符或文件名吗? 放松,单击鼠标中键(鼠标中键是什么?就是鼠标中间的按键或者按下滚轮也可以)或者鼠标右键从弹出的菜单中选择“粘贴”即可。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== 节省输入 ==== | ||
{| cellspacing="0" border="1" | {| cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Up Arrow''' or '''ctrl+p''' | | '''Up Arrow''' or '''ctrl+p''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 滚动显示你之前输入的命令.(译者注,与msdos相似) |
|- | |- | ||
| '''Down Arrow''' or '''ctrl+n''' | | '''Down Arrow''' or '''ctrl+n''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 回到较近的命令.(与up arrow相反,反方向滚动) |
|- | |- | ||
| '''Enter''' | | '''Enter''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 找到你要的命令时按回车确认<br> |
|- | |- | ||
| '''tab''' | | '''tab''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 一个非常有用的功能。如果只有一个选项,则自动补全命令或文件名;否则给出所有选项的列表。 |
|- | |- | ||
| '''ctrl+r''' | | '''ctrl+r''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 搜索你已经输入的命令.当你已经输入了一条很长很复杂的命令并且要重复它时, 使用这个按键组合,然后输入命令的一部分将会从你的集合历史中搜索. 找到它后,只要轻轻按下回车 |
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== 更改命令 ==== |
| − | + | 不能用鼠标。你可以用左/方向键来移动。当游标在你想让它在的地方时,输入 ''inserts'' text - ie 它不会改写那儿的文字。 | |
{| cellspacing="0" border="1" | {| cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''ctrl+a''' or '''Home''' | | '''ctrl+a''' or '''Home''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 移动游标到行首. |
|- | |- | ||
| '''ctrl+e''' or '''End''' | | '''ctrl+e''' or '''End''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 移动游标到行尾. |
|- | |- | ||
| '''ctrl+b''' | | '''ctrl+b''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 移动游标到上一个或当前单词的前面. |
|- | |- | ||
| '''ctrl+k''' | | '''ctrl+k''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 删除从当前游标到行尾的文字. |
|- | |- | ||
| '''ctrl+u''' | | '''ctrl+u''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 删除当前整行. |
|- | |- | ||
| '''ctrl+w''' | | '''ctrl+w''' | ||
| − | | | + | | <br> |
| − | | | + | | 删除游标前的单词. |
|} | |} | ||
| − | === | + | ===采用更多方法运行终端=== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | 您也可以使用功能鍵來運行一個以上的終端 - 多標簽的方式[Shift + Ctrl + T] 或者以多個獨立窗口的方式[Shift + Ctrl + N] | |
| − | + | === 更多信息 === | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * [[UbuntuHelp:AptGetHowto/zh|apt-get 使用指南]] - 用apt-get在命令行下安装软件包 | |
| + | * [[UbuntuHelp:Repositories/CommandLine|Commandline Repository Editing]] - 在命令行下添加 Universe/Multiverse 软件库。 | ||
| + | * [[UbuntuHelp:Grep/zh|grep Howto]] - grep 是一个非常强大的命令行下的搜索工具。 | ||
| + | * [[UbuntuHelp:CommandlineHowto]] - 比本文要长,也要完整很多的基础命令指南,至今为止,仍未完成。 | ||
| + | * [[UbuntuHelp:HowToReadline]] - 针对命令行的更高级定制的信息。 | ||
| − | + | 关于Linux命令行的更详细指南,请参阅: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | * http://linuxcommand.org/ - 基础 BASH 指南,包括 BASH 脚本。 | ||
| + | * http://linuxsurvival.com/index.php - java基础指南 | ||
| + | * http://rute.2038bug.com/index.html.gz - 系统管理相关的大量文档,几乎全部使用命令行。 | ||
| + | * Very good! | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Head back to [[UbuntuHelp:UserDocumentation|UserDocumentation]] | Head back to [[UbuntuHelp:UserDocumentation|UserDocumentation]] | ||
| − | [[Category:UbuntuHelp]] | + | [[Category:UbuntuHelp]][[category:入门]][[category:系统]] |
2011年10月8日 (六) 19:29的最新版本
| 点击翻译: |
English • 中文 |
目录
为什么使用终端?
Linux下面有多种GUI(图形用户界面),可以在其下点击鼠标,拖拽,能够很好的工作却不需要一次读很多文档.而传统的Unix环境是 CLI(命令行界面),即在命令行下键入命令,执行想要的操作。相比之下,这种方式执行起来更快,功能也更强,不足之处是用户需要了解相关操作的命令。 --摘自 man intro(1) 在做某些任务,特别是系统配置等任务时使用终端是很有意义的,或许在帮助页或 论坛中你已经看到过类似这样的指令:
sudo gobbledegook blah_blah -w -t -f aWkward/ComBinationOf/mixedCase/underscores_strokes/and.dots
通常假设你知道怎么使用终端-而且任何人都能输入和退格。但有一些快捷的方法使你的生活更容易一些:
- 怎样在终端窗口中移动和编辑你输入的文字。
- 一些基本的Linux命令。
- 打开终端的不同方法,怎样同时操作好几个终端,等等。
使用本页将:
- 本文将指导您熟练掌握基本的 GNU/Linux shell 命令。
- 本文并不是命令行的完整教程,仅仅是对 Ubuntu图形界面工具的补充。
- 所有命令都用黑体标明。
- 需要键入的命令用“引用黑体”标明。
- 本文的所有命令都要在终端下执行。
- 注意:Linux是大小写敏感的。User,user,USER在Linux是不同的。
启动终端
在 Gnome (Ubuntu) 中
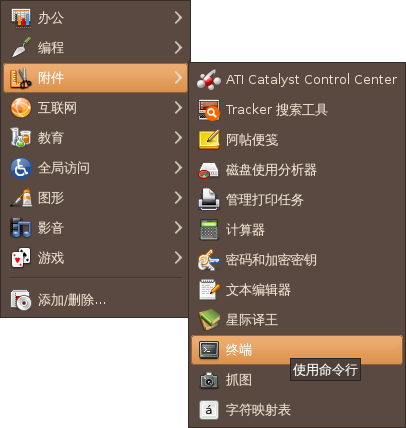
- 从“应用程序”菜单启动
- 终端位于 应用程序 -> 附件 -> 终端。
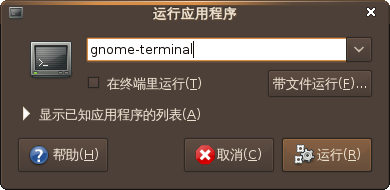
- 使用命令启动
- 按Alt-F2,输入 gnome-terminal 回车
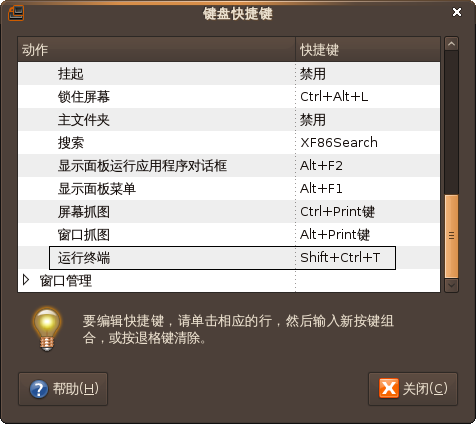
- 使用热键
- 在键盘快捷键中设置自己习惯使用的热键,每次按热键就可启动终端。
在 Xfce (Xubuntu) 中
终端位于 应用程序 -> 系统 -> 终端。
在 KDE (Kubuntu) 中
终端位于 K菜单 -> 系统 -> 终端程序 (Konsole)。
命令行
sudo:需要提升权限执行的命令
- 如果您所在的目录或想操作的文件不在您的帐户所在的目录,下面的大多数命令都需要使用 sudo命令。这是一个特殊的命令,它给你临时的权限来修改系统设置。终端会询问你的密码。sudo 使用详情请参阅RootSudo
文件 & 目录类命令
- pwd:pwd 命令查看您当前所处的路径(pwd 代表 "打印当前工作目录")。例如:在桌面文件夹中执行 "pwd" 命令将输出 "~/Desktop"。注意,Gnome 的终端在窗口标题中也会显示这一信息-具体请看本页顶部的截屏图片。
- ls:ls 命令列出当前目录下的文件(和目录)。使用特定的参数,您可以查看文件的大小,创建时间,权限等。例如:"ls ~"会列出您的home目录中的文件(和目录)。
如:ls -a表示“列出所有文件,包括以 "." 开头的隐含文件”。
- cd:cd命令用来改变当前工作目录。当您打开一个终端的时候,您就位于您的home目录中。如果想要切换到其它的目录,就要用 cd命令。例如:
- 进入root目录,输入 "cd /"
- 进入到您自己的目录(home目录),输入 "cd"
- 进入当前目录的上一层目录,输入 "cd .."(译者注:cd 与 .. 之间有空格)
- 进入前一个操作的目录,输入 "cd -"
- 一次进入多层目录,输入 "cd /var/www",将会直接切换到/var的子目录/www中。另一个例子, "cd ~/Desktop"将会进入到您的桌面目录
- cp:cp命令用来复制文件。例如:"cp file foo"命令将会创建一个"file"的精确的副本,并命名为"foo",而 "file"不会有任何变化。如果是复制目录,那就得用"cp -r directory foo"(递归地复制)。
- mv:mv命令将文件移动到另一个位置或者给文件更名。看下面的例子:"mv file foo"命令会将文件"file"更名为"foo"。"mv foo ~/Desktop"会将文件"foo"移动到桌面目录,但不会更名。如果想更名,你必须要指定一个新的名字。
- 为了输入方便,您可以用 '~' 符号来代替您的home目录。
- 如果在用mv命令的时候前面加上了sudo,那么“~“这个符号将可以正常使用,终端会把他替换成你自己(普通用户)的home目录。而如果你用”sudo -i“或者”sudo -s“,'sudo su'打开了一个root用户的终端,那么这时”~“将指代root用户的home目录,而非你自己的。
- rm:这个命令用来移动或删除文件。对于非空的目录,需要rm -r才能删除。
- rmdir:命令rmdir只能用来删除“空”目录。
- mkdir:mkdir 命令用来创建目录。例如:"mkdir music"将会创建一个 music 目录。
- man:man 命令用来显示其它命令的手册页。执行 "man man"可以查看到 man自己的信息。通过 "Man & Getting Help"能够分页显示更多的信息。
系统信息类命令
- df:df命令用来查看各个文件系统当前的空间使用状况。"df -h"可能是最有用的选项了-它以M和G为单位输出,而不是以块为单位。(-h 的含义是“便于阅读”)
- du:du命令可以显示某一个目录使用了多少磁盘空间。它可以显示该目录中的各个子目录分别使用了多少空间,也可以显示当前目录一共占了多少空间。例如:
user@users-desktop:~$ du /media/floppy 1032 /media/floppy/files 1036 /media/floppy/ user@users-desktop:~$ du -sh /media/floppy 1.1M /media/floppy/
- -s 代表”概况、总览“,-h 则代表”易于人阅读“。
- free:free命令用来查看系统中使用和剩馀的内存情况。"free -m" 将结果以M为单位输出,这对现在的计算机来说非常有用。
- top:top 命令用来查看linux系统的信息,运行着的进程和系统资源,包括 CPU、内存以及交换分区使用情况和运行着的任务的总的数量。退出 top ,按"q"。
- uname -a:uname命令的 -a 参数用来查看系统的所有信息,包括 机器名,内核名称 & 版本 和一些其它的细节。它最大的用处是用来查看当前所用内核的信息。
- lsb_release -a:lsb_release命令的-a参数查看当前运行的linux的版本信息,例如:
user@computer:~$ lsb_release -a No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Ubuntu Description: Ubuntu 6.06 LTS Release: 6.06 Codename: dapper
- ifconfig显示当前系统的网络接口信息。
添加新用户
- "adduser newuser"命令用来创建一个用户名为"newuser"的新用户,为新用户 newuser 创建一个密码,使用如下命令"passwd newuser"。
选项
命令的默认操作常常会被指定一个确定的 --参数所修改。例如ls命令有一个-s参数,因此 "ls -s"就会额外的显示出文件的大小。它也有一个 -h参数,将文件的大小以很好的可读性的格式输出。参数可以以簇聚合,比如 "ls -sh"和"ls -s -h"的效果相同。大多数的参数都很长,两个破折号前缀代表一个参数,所以"ls --size --human-readable"也和上面得命令相同。
'Man' 和 获得帮助
man command, help command,info command and command --help是命令行下面最重要的工具。
在linux下面,几乎每一个命令和每一个应用程序都会有一个man(manual)文件,所以只要简单的键入"man "command""就能看到这个命令的手册页。例如,"man mv"会打开mv (Move) 的手册页。
利用键盘上的方向键移动手册页面,用"q"退出。
"man man"会查看man命令的手册页,这里是一个很好的开始!
"man intro"也非常有用 -它能够查看 "用户命令介绍",写的非常好!是一份很简单的linux命令的介绍。
还有一个就是info命令了,它通常比man还深入。输入"info info"命令可得到info页的介绍。
一些软件开发人员喜欢用 info 而不是 man (例如Debian和GNU开发人员)。所以,如果你发现一个不很常见的命令或者程序没有 man 页面,那么就试试 info 页面。
几乎所有的命令都能接受一个-h(或 --help)选项,能够输出命令的简要的描述和参数,然后自动退回命令提示符。可以输入"man -h"或"man --help"查看。
警告:一些软件不认为 -h 选项代表帮助,虽然少但是存在这种情况。这时候可以先试试 man 或者 info 页面,以及使用较长的选项 --help。
搜索man文档
如果您不确定用哪个命令或程序,您可以试试搜索man文件。
- man -k foo 会搜索关于foo的man文件。试试看"man -k nautilus"是怎样的。
- 注意:这同apropos 命令是一样的。
- man -f foo 仅仅搜索系统man文件的标题。试试"man -f gnome"。
- 这个同 whatis命令是相同的。
<Why the man / info command are English, beyond many people's comprehension including me. Can we develop a native(i.e. Chinese) edition?>
其他有用的东西
更加漂亮的使用手册页面
安装了Konquerer的用户会高兴的发现他们可以在Konqueror的地址栏里面输入“man:/command”,达到类似在一个web浏览器中像浏览网页一样的阅读或搜索“man使用手册”的相关信息,通过选择字体与颜色(系统配置中的字体与颜色)来达到一定程度的美化,这会让部分需要阅读大量“man使用手册”内容的用户感到一些轻松。
命令行中粘贴
通常,你会碰到这种情况:需要把一些网页中看到的命令粘贴到命令行窗口(也就是“终端”)里面,但你会奇怪为什么在网页上使用了“Ctrl+C”进行了复制,然后在“终端”里面使用“Ctrl+V”(粘贴)却不好使,非得自己亲自动手敲那些繁琐的命令字符或文件名吗? 放松,单击鼠标中键(鼠标中键是什么?就是鼠标中间的按键或者按下滚轮也可以)或者鼠标右键从弹出的菜单中选择“粘贴”即可。
节省输入
| Up Arrow or ctrl+p | |
滚动显示你之前输入的命令.(译者注,与msdos相似) |
| Down Arrow or ctrl+n | |
回到较近的命令.(与up arrow相反,反方向滚动) |
| Enter | |
找到你要的命令时按回车确认 |
| tab | |
一个非常有用的功能。如果只有一个选项,则自动补全命令或文件名;否则给出所有选项的列表。 |
| ctrl+r | |
搜索你已经输入的命令.当你已经输入了一条很长很复杂的命令并且要重复它时, 使用这个按键组合,然后输入命令的一部分将会从你的集合历史中搜索. 找到它后,只要轻轻按下回车 |
更改命令
不能用鼠标。你可以用左/方向键来移动。当游标在你想让它在的地方时,输入 inserts text - ie 它不会改写那儿的文字。
| ctrl+a or Home | |
移动游标到行首. |
| ctrl+e or End | |
移动游标到行尾. |
| ctrl+b | |
移动游标到上一个或当前单词的前面. |
| ctrl+k | |
删除从当前游标到行尾的文字. |
| ctrl+u | |
删除当前整行. |
| ctrl+w | |
删除游标前的单词. |
采用更多方法运行终端
您也可以使用功能鍵來運行一個以上的終端 - 多標簽的方式[Shift + Ctrl + T] 或者以多個獨立窗口的方式[Shift + Ctrl + N]
更多信息
- apt-get 使用指南 - 用apt-get在命令行下安装软件包
- Commandline Repository Editing - 在命令行下添加 Universe/Multiverse 软件库。
- grep Howto - grep 是一个非常强大的命令行下的搜索工具。
- UbuntuHelp:CommandlineHowto - 比本文要长,也要完整很多的基础命令指南,至今为止,仍未完成。
- UbuntuHelp:HowToReadline - 针对命令行的更高级定制的信息。
关于Linux命令行的更详细指南,请参阅:
- http://linuxcommand.org/ - 基础 BASH 指南,包括 BASH 脚本。
- http://linuxsurvival.com/index.php - java基础指南
- http://rute.2038bug.com/index.html.gz - 系统管理相关的大量文档,几乎全部使用命令行。
- Very good!
Head back to UserDocumentation