Wubi
来自Ubuntu中文
| DVD 安装 | LiveCD 试用 | LiveCD 安装 | U 盘安装 | Wubi 安装 | 硬盘安装LiveCD |
目录
- 1 引言
- 2 安装
- 3 卸载
- 3.1 如何卸载 Wubi?
- 3.2 如何手动卸载 Wubi?
- 3.3 如何重装 Wubi?
- 3.4 不能启动 Ubuntu
- 3.5 格式化 swap 文件时安装错误
- 3.6 我怎样把 Ubuntu 作为默认引导选项?
- 3.7 我可以备份安装文件吗?
- 3.8 虚拟磁盘应该要多大?
- 3.9 我怎样才能移植到一个真实的分区,甚至完全摆脱 Windows?
- 3.10 How do I resize the virtual disks?
- 3.11 How do I create a virtual disk in Ubuntu?
- 3.12 How do I create a virtual disk in Windows?
- 3.13 How do I access the Windows drives?
- 3.14 How can I access the Wubi files from Windows?
- 3.15 How can I access my Wubi install and repair my install if it won't boot?
引言
安装
完成后程序会要求您重启计算机。重新启动后在启动选单中选择 Ubuntu。安装操作将继续执行 10-15 分钟并再次重启计算机。至此安装完毕,您可以在启动选单中选择 Ubuntu 并开始使用。
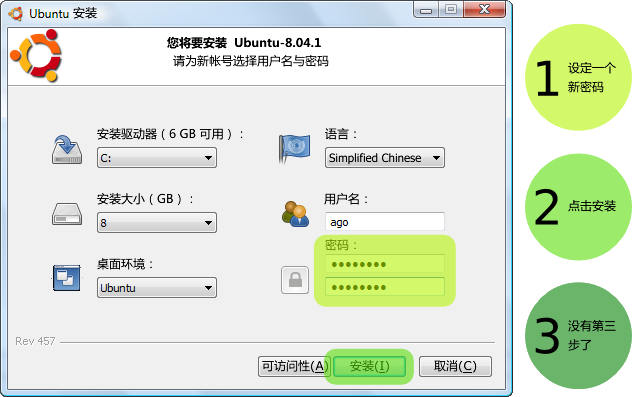
标准安装的默认设置可以满足大部分用户的使用要求。这个可以修吗?
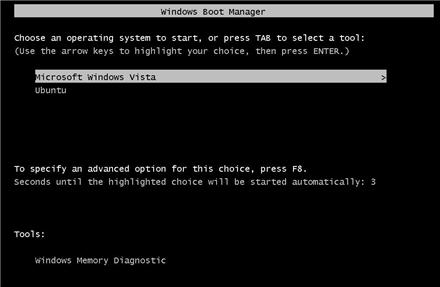
如何选择运行 Windows 或 Ubuntu?
重启后,您可以在启动选单选择运行 Windows 或 Ubuntu。
如何强制 Wubi 安装在内存 <= 256MB 的计算机上?
您可以使用“--skipmemorycheck”参数运行 Wubi。在此情况下安装工具可能无效。
如何强制 Wubi 安装在空闲磁盘空间 < 5GB 的计算机上?
您可以使用“--skipspacecheck”参数运行 Wubi。安装最少要求 3GB 磁盘空间(加上存放 ISO 的空间),不要在更小的空间上尝试...
如何强制 Wubi 跳过 md5 校验?
您可以使用“--skipmd5check”参数运行 Wubi。
安装被中断后如何处理?
您应当在 Windows 中重新运行 Wubi(程序可能要求您先卸载 Wubi)。
卸载
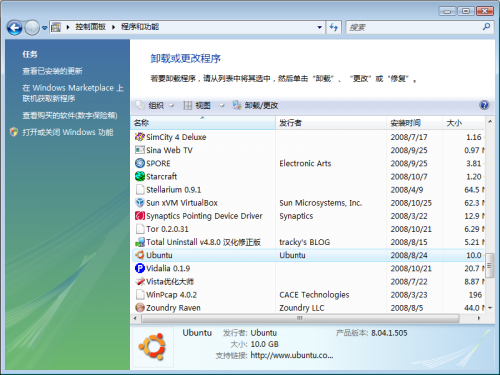
如何卸载 Wubi?
在“添加删除程序”(Vista 为“程序和功能”)里运行卸载工具。或使用 C:\ubuntu\uninstall.exe(如果安装在其他分区,请将 C: 替换成相应盘符)。
如何手动卸载 Wubi?
删除 C:\ubuntu(7.04 版为 C:\wubi,如安装在其他分区,请删除相应分区内的文件)及 C:\wubildr*(包括 C:\wubildr 及 C:\wubildr.mbr)。
对于 Windows XP,您需要编辑 C:\boot.ini 并删除包含 Ubuntu/Wubi 的行。对于 Vista,您可以使用 EasyBCD 编辑启动菜单。或者可以通过 控制面板 > 系统 > 高级 > 启动和故障恢复 点击“编辑”修改启动菜单(仅限 XP)。对于 Windows 98,您需要编辑 C:\config.sys,并删除 Wubi 的区段。
删除以下注册表键:HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\Wubi,即可将 Wubi 从添加删除列表中移除。
如何重装 Wubi?
再次运行 Wubi.exe。Wubi 将检测现有的安装,并显示卸载的选项。您应当备份安装文件(ISO 镜像),以免重新下载的麻烦。请注意重装后,虚拟磁盘(root.disk)将被复位。
不能启动 Ubuntu
如果 Windows 没有正常关机,Ubuntu 可能不能启动。遇到这种情况,您应当在 Windows 中检查文件系统(目前 Linux 还没有与 chkdsk 相应的工具)。如果 Wubi 启动失败,请启动 windows,在安装 Ubuntu 的分区运行 chkdsk /r,正常关闭计算机并再次尝试启动 Ubuntu。
请注意 Windows 有时会将文件移动至一个隐藏文件夹 c:\found.000。您需要有 c:\ubuntu\disks\root.disk 及 c:\ubuntu\disks\boot 才能启动。如果这些文件不在该位置,请到 found.000 中寻找。您需要首先设置 windows explorer 以便显示隐藏文件,然后将文件从 found.000 移动回原来的路径。
请确认您没有在磁盘阵列或加密磁盘中安装。并且没有使用 Alternate 或 DVD ISO 安装。
格式化 swap 文件时安装错误
如果安装在格式化 swap 虚拟磁盘时失败,表明您的磁盘充满了磁盘碎片。请卸载安装,使用 jkdefrag 在目标分区清理磁盘碎片,然后重新使用 wubi 安装。
我怎样把 Ubuntu 作为默认引导选项?
Ubuntu 未安装为默认的引导选项,你必须在 Windows 引导菜单中选择。要更改这个,在 Windows XP 中转到 控制面板 > 系统 > 高级 > 启动和恢复 并编辑“默认操作系统”,你还可以更改等待时间。
我可以备份安装文件吗?
是的,只需复制 C:\ubuntu\disks\root.disk 到其他的地方即可(在 7.04 版本中该文件是 C:\wubi\disks\*.virtual.disk)。旧的安装文件可以挂载(mount)在 Ubuntu 中,所有相关数据都可以复制到新的安装。
虚拟磁盘应该要多大?
默认大小是根据您的可用空间自动计算得出的,您可以在设置中更改它。实际上,空间不会被完全使用,一个标准的系统安装小于 3 GB,包括所有预安装的软件(office 套件、 游戏、 图形应用程序,等等),但您一旦开始安装额外的软件,2-3 GB 的虚拟磁盘会很快用完空间。大多数情况下 8 GB 应该足够了。请记住 FAT 文件系统上的虚拟磁盘不能大于 4 GB (Wubi 将把大于 4G 的空间拆分成多个虚拟磁盘)。另外,除了虚拟磁盘本身需要占用的空间外,记得 Wubi 需要额外的可用空间,这是因为它需要获取 ISO (700 MB) 文件,再加上一些辅助文件。所以如果您的可用空间少于 5 GB,Wubi 将不能安装。
我怎样才能移植到一个真实的分区,甚至完全摆脱 Windows?
已有的 Wubi/Lubi 安装可以通过 LVPM 升级到一个在专用分区上的安装。LVPM 的主站在 http://lubi.sourceforge.net/lvpm.html 而指南和支持论坛在 http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=438591。 另外,下列脚本也可以用于 Wubi 8.04. 下载attachment:wubi-move-to-partition 打开一个终端并运行:
sudo sh wubi-move-to-partition /dev/sda9 /dev/sda10
替换其中的 /dev/sda9 为你希望移植 Wubi 安装到的分区,而 /dev/sda10 是适当的 swap 分区(你完全可以省略第二个参数,在这种情况下,没有 swap 会被设置)。两个分区必须已经存在,并且为空白(你可以使用任何分区工具,譬如 gparted 来预先创建它们)。注意,脚本将会安装 grub 作为主要的 bootloader 来替换已有的 bootloader,并且比较难以撤销更改(如果事情不如你所愿的发展,你将必须从 Live CD 引导并手动替换/编辑 bootloader)。另外还要注意,如果你有多个硬盘,磁盘的顺序可能需要手动调整。
How do I resize the virtual disks?
You can use LVPM, at http://lubi.sourceforge.net/lvpm.html As an alternative, you can use the following script to move /home or /usr to a dedicated virtual disk. Download attachment:wubi-add-virtual-disk, open a terminal and run:
sudo sh wubi-add-virtual-disk /home 15000
Where the first argument is the directory to move to a new dedicated disk, and the second argument is the size in MB. The 2 directories you are most likely to migrate are /home (if you have a lot of user data) and /usr (if you installed a lot of software). You should now reboot. If you are happy with the result, you can now remove /home.backup. To undo the changes remove /home, copy rename /home.backup to /home and remove the /home line in /etc/fstab.
How do I create a virtual disk in Ubuntu?
Open a terminal (Applications -> Accessories -> Teminal), and enter these commands (this will create a 10 GB extra.virtual.disk, adjust line 2 to change these):
cd /host/ubuntu/disks sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=extra.disk bs=1MB count=1 seek=10000 sudo mkfs.ext3 -F extra.disk
How do I create a virtual disk in Windows?
You can use qemu-img for that. Another dirty trick (but working) is to copy any other file of the desired size to c:\wubi\disks and rename it "root.disk", "home.disk", "swap.disk" or "extra.disk". That's the wubi equivalent of buying (and installing) a new hard disk ;)
If you are running Windows XP (may work in Windows 2000 and Vista as well) you can create a file by using the fsutil that is included with Windows. The command format is fsutil file createnew filename filesize where filename is the file you wish to create and filesize is the size of the file to be created in bytes.
How do I access the Windows drives?
The Windows partition where you installed Wubi is available as /host within Ubuntu All the other partitions will be available under /media/ If you are using Wubi-7.04 (7.10 and 8.04 users can skip this), write support for ntfs is disabled by default, to enable it:
- Make sure you have internet access (see the network icon on the top right)
- Open the "Applications" menu and select "Add/Remove..."
- In the listbox on the right select: "Show All Available Applications"
- Search for "NTFS" and select "NTFS Configuration Tool". Click OK to install it
- Run the configuration tool under Applications > System Tools > NTFS Configuration Tool
- Select "Enable write support for internal device". Click OK to set it up.
How can I access the Wubi files from Windows?
There are a few Windows applications that can mount ext2-based file systems. See for instance:
The relevant Wubi files you need to access are located under C:\ubuntu\disks\
How can I access my Wubi install and repair my install if it won't boot?
Boot the Ubuntu Desktop CD, or another LiveCD, then mount the windows partition:
sudo mkdir /win sudo mount /dev/sda1 /win
Replace sda1 with the appropriate device (a == disk, 1 == partition number), then mount the virtual disk therein
sudo mkdir /vdisk sudo mount -o loop /win/ubuntu/disks/root.disk /vdisk
Now the content of the virtual disk will be visible under /vdisk. 7.04 users will have to install ntfs-3g first and specify it as fstype to gain r/w access. To check the filesystem you can use:
sudo fsck /win/ubuntu/disks/root.disk
